Computer hardware, firmware, peripherals, and software work together to input, process, store, and output data.
- Hardware refers to a computer’s physical components.
- Software refers to the system software and software applications that run on a computer and enable the hardware to perform various tasks.
- Firmware is a special type of software that is embedded in hardware components to control their basic functions.
- Peripherals are external devices that connect to a computer and provide it with additional functionalities.
The invention of the computer cannot be attributed to a single individual. The evolution of computers from early mechanical calculating machines to today’s advanced digital systems involved the work of numerous scientists, engineers, and mathematicians.
Charles Babbage (1791 – 1871) is often referred to as the “father of the computer.” He is credited with promoting the concept of programming and the idea of automating computation.
Ada Lovelace (1815 – 1852) wrote what is often regarded as the first algorithm intended to be processed by a machine.
George Boole (1815 – 1864) developed a logic system that laid the groundwork for the binary system that’s used in computer programming and digital circuit design.
Alan Turing (1912–1954) is credited with formalizing the concepts of “algorithm” and “computation” with the invention of his Turing machine. He also made contributions to the field of artificial intelligence and proposed a method for determining whether a machine is capable of intelligent behavior that is indistinguishable from that of a human.
John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry (1942) designed and built one of the first electronic digital computers. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC), which was designed primarily for solving linear algebraic equations, used binary digits and had the ability to perform simultaneous operations in parallel.
John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert (1945) designed and built the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), one of the earliest electronic general-purpose digital computers. ENIAC could be reprogrammed to solve a wide range of numerical problems.
John von Neumann (1903-1957) proposed the principle of stored programs in 1945. This innovation is often considered to be as significant as the transition from mechanical to electronic computing.
John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley invented the transistor in 1947. Transistors, which are used to control and manipulate electrical signals, began to replace vacuum tubes in computers in the late 1950s.
Robert Noyce’s idea for putting an integrated circuit (IC) on a silicon chip in 1959 made it possible to mass produce integrated circuits and paved the way for miniaturizing computer components.
Ted Hoff, Federico Faggin, Stanley Mazor, and Masatoshi Shima designed the first commercially available microprocessor, which was released by Intel in 1971. The microprocessor’s ability to perform a variety of tasks on a single chip helped make personal computers (PCs) and smart devices possible.
What Can a Computer Do?
A computer can perform a vast range of tasks, depending on its design and the software it runs. Common capabilities include:
- Performing complex mathematical calculations at high speed.
- Creating, tracking, storing, and transferring
- Facilitating creativity, communication, collaboration, and online learning.
- Providing access to the World Wide Web.
- Conducting complex simulations and analysis for scientific research.
- Facilitating machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence.
- Controlling and monitoring other computer systems.
- Playing streaming media and computer video games.
- Managing digital financial transactions.
- Automating business processes.
- Digitizing health care and supporting the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
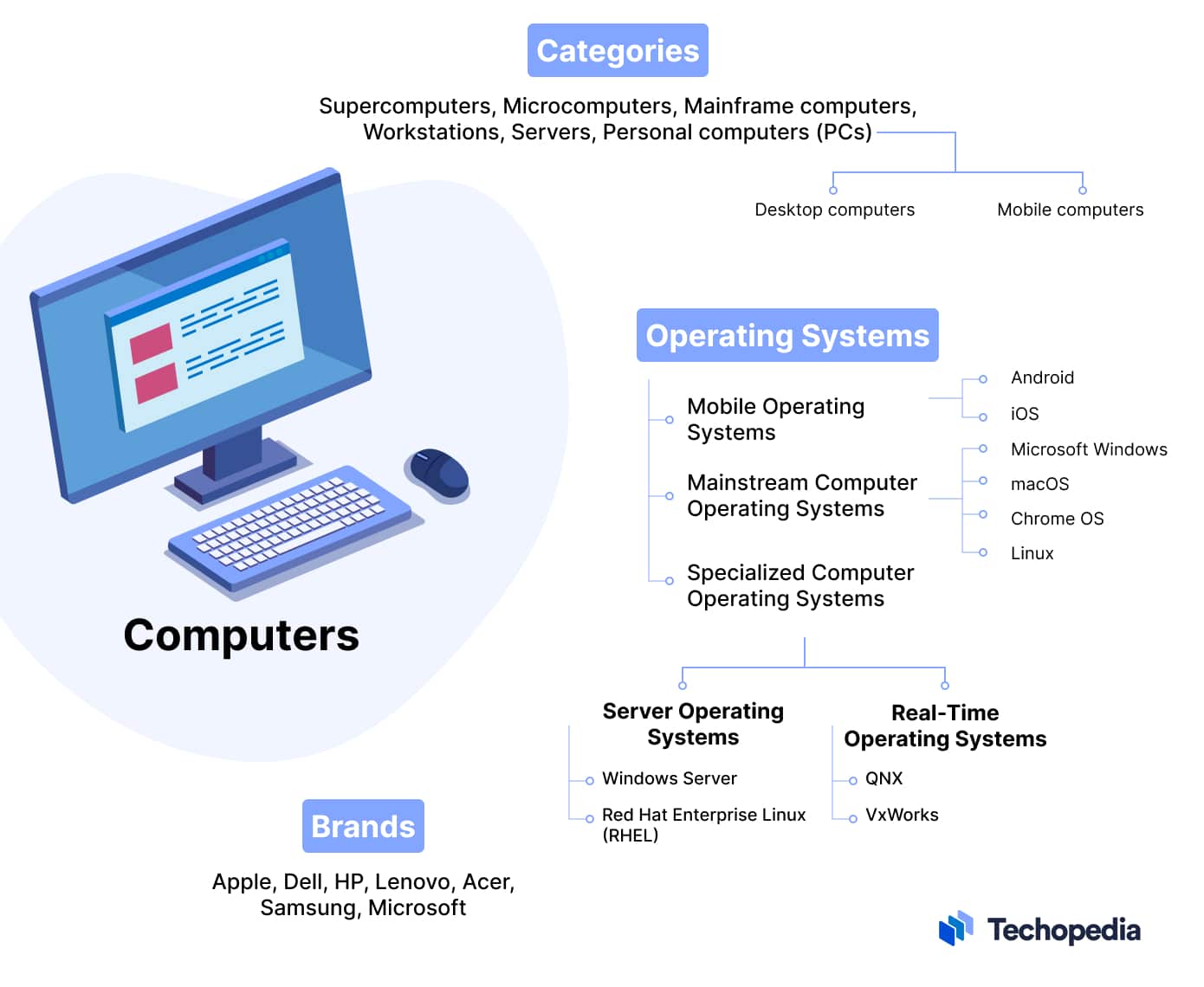
What are the Different Types of Computers?


0 Comments